Leave vacuum casting to
Umehara Model!!
The advantage of vacuum casting is its low initial investment cost. Therefore, vacuum casting is suitable for producing prototypes in quantities up to several dozen.
Vacuum casting is a method of duplicating resin products by pouring resin into a mold inside a chamber close to a vacuum state.
The molds used for casting mainly use silicone rubber, and the resins for cast products are urethane-based or epoxy-based resins.
It is used in various applications, including prototype production of automotive parts, OA equipment parts, amusement equipment parts, and more.

Situations Suitable for Vacuum Casting
- - You want to produce multiple copies of the same product, but not enough to warrant making a metal mold.
- - You want to produce multiple copies of the same product, but cannot meet the deadline with methods like metal molds or machining.
- - You want to make the same product with resins that have different properties.
Vacuum casting is utilized in various situations like these.
Advantages

- Realizing Short Delivery Times and Low Cost By using simple silicone rubber molds, we achieve short delivery times and low costs.

- Abundant Variety of Materials In vacuum casting, we use two-component thermosetting urethanes or epoxies, and their range of physical properties is very diverse.
(We offer materials with physical properties that closely resemble actual molded products like ABS, PP, acrylic, rubber, etc.)

- Coloring of Resin Materials To get closer to the final product, it is possible to mix pigments into the resin materials for coloring.

- Insert Molding and Two-Color Molding It is possible to perform molding with insert nuts or terminals inserted.
Also, it is possible to mold different resins, such as soft and hard materials, into a single piece.

- Regarding the Design Surface of Cast Products By applying surface treatments such as painting to the master model before creating the rubber mold, it results in a finish similar to molded products.
Disadvantages

-
Mismatch with Final Product Materials While there is a wide variety of physical properties, in vacuum casting, the resins that can be used are limited to urethane-based or epoxy-based due to the method.
Therefore, it is not very suitable for strength testing.

- Unsuitable for Precise Dimensional Accuracy Since the molds are made of silicone, fine precision is inferior compared to machining or metal molds.

-
Unsuitable for Mass Production Due to the silicone rubber molds, only about 20 shots can be taken per mold.
(If you want to produce transparent products, it becomes about 10 to 15 shots.)
* In some cases, "machining" may be more suitable. Click here for details >>
Here, we introduce urethane-based materials.
| Type Name | Features |
|---|---|
| ABS Type | A resin with texture and physical properties similar to ABS resin. (Standard colors: Ivory, Black, White) |
| PP Type | A resin with texture and physical properties similar to PP resin. (Standard colors: Natural, Black) |
| Acrylic Type | A resin with texture and physical properties similar to acrylic resin. (Standard color: Transparent) |
| Rubber Type | A rubber-like material. Hardness can be adjusted from 20 to 90. (Standard color: Black) |
| High Heat Resistance Type | A resin with heat resistance of about 140°C. (Standard colors: Light Yellow, Black) |
| Flame Retardant Type | A material certified as UL V-0. (Standard color: White) |
We can also research materials not listed here. In addition, colorings other than standard colors are available, so please let us know.
First, vacuum casting requires a product called a "master model."
This is mainly made by machining or modeling. If you have the original product you want to duplicate, that product is acceptable.
Based on this "master model," we create the rubber mold.
The price in vacuum casting is calculated as follows.
- Initial Cost
- Master Model + Rubber Mold
- Product Cost
- Casted Products x Quantity
The master model, rubber mold, and cast products vary depending on their size and shape.
If the quantity is small, we recommend "machining."

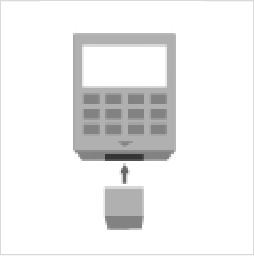
- 1. Attach the gate, which will be the inlet for the casting resin, to the prototype.

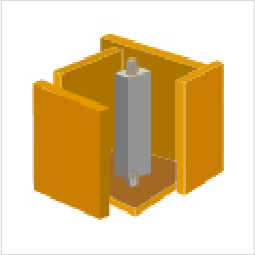
- 2. Adhere the gate to the mold frame and assemble the mold frame.


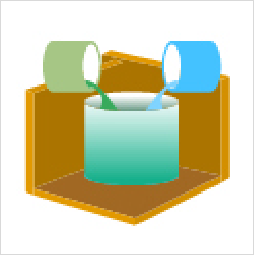
- 3. While vacuum degassing, mix the base material and curing agent thoroughly.



- 4. Further degas under reduced pressure.


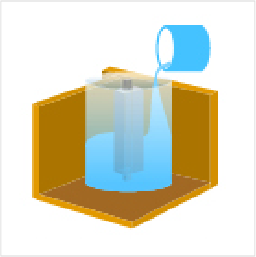
- 5. Pour liquid silicone rubber until the prototype is completely submerged.



- 6. After vacuum degassing, remove the mold frame, cut open the silicone rubber mold, and take out the prototype.


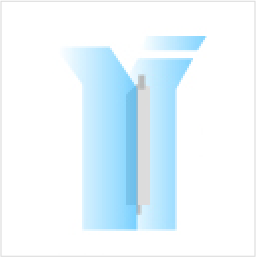
- 7. Once cured, remove the mold frame, cut open the silicone rubber mold, and take out the prototype.



- 8. Spray release agent onto the silicone rubber mold as needed.


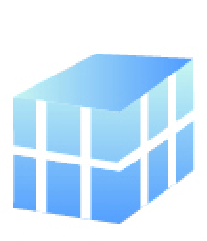
- 9. Align the molds, secure them firmly with tape or clamps, and attach the resin reservoir to the gate section.



- 10. Vacuum degas the required amount of casting resin.


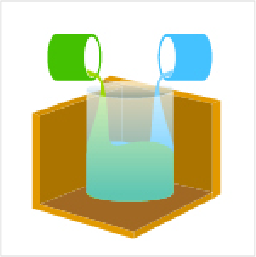
- 11. Mix the degassed casting resin.


- 12. Under reduced pressure, pour the mixed casting resin from the resin reservoir into the mold.



- 13. When the air pressure is restored, the resin flows into the mold. Cure the resin under specified conditions.



- 14. Break the cured mold and take out the cast product. Cut off the gate and finish with a file, etc.

 +81-27-637-5700
+81-27-637-5700











